One of the expected benefits of Open RAN and the use of RIC is increased energy efficiency. But promises are just that unless you can validate the anticipated effect through reliable testing. Towards this end, we have successfully continued our collaboration with Rimedo Labs on this subject, aiming to provide testing solutions that are valuable for the entire industry, furthering the Open RAN ecosystem, and enabling innovation in RAN.
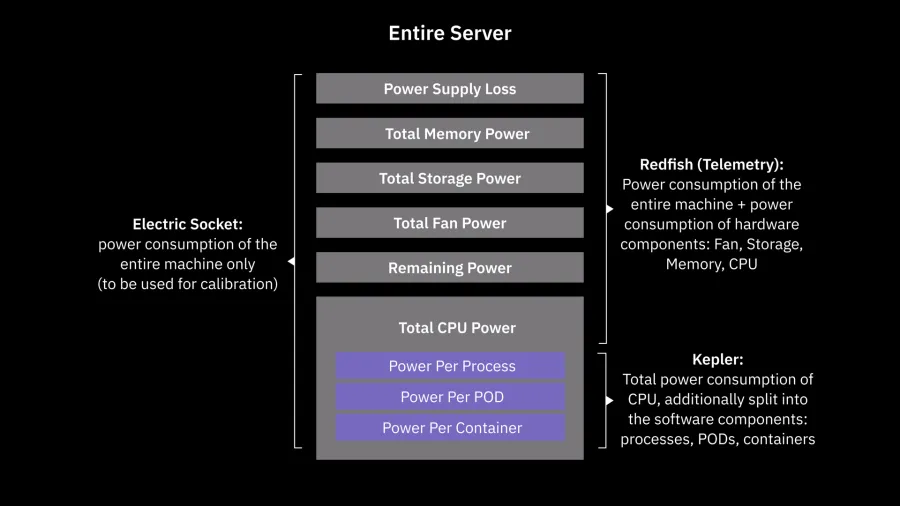
The tests were conducted in the i14y Lab, using Redfish and Kepler for measuring the power consumption of our DELL R750 server hosting the Rimedo Labs and Cell On/Off Switching (COOS) rApp, along with O1-termination-related VNFs (also provided by Rimedo Labs), operating under a RAN emulated by Keysight RICTest, including the O-RAN-compliant O1 interface, and used to interact with tens of cells and hundreds of UEs.